Electric transfer cart Key Considerations
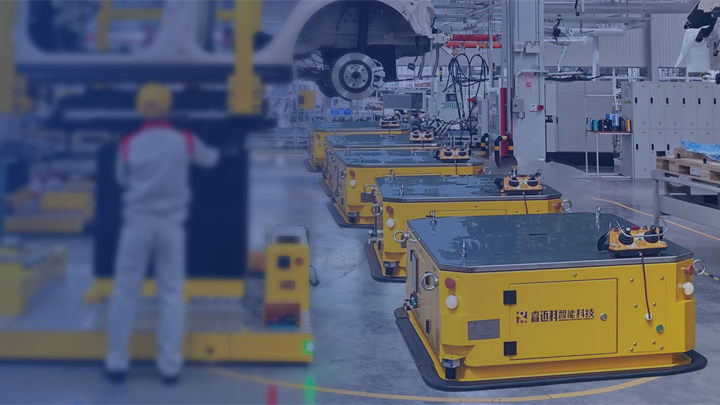

Determine the Usage Scenario
Indoor/Outdoor: Select an appropriate model based on the working environment. For example, outdoor scenarios may require considerations such as rainproofing, dust resistance, and ground adaptability.
Space Constraints: If the working space is limited, choose a model with a small turning radius and high flexibility.
Clarify Load Requirements
Load Capacity: Select a suitable electric transport carts based on the weight of the transported goods.
Customizable for heavy duty ranging from 1 to 1000 tons
Cargo Dimensions: Ensure the platform size and height of the transfer trolley are compatible with the cargo.
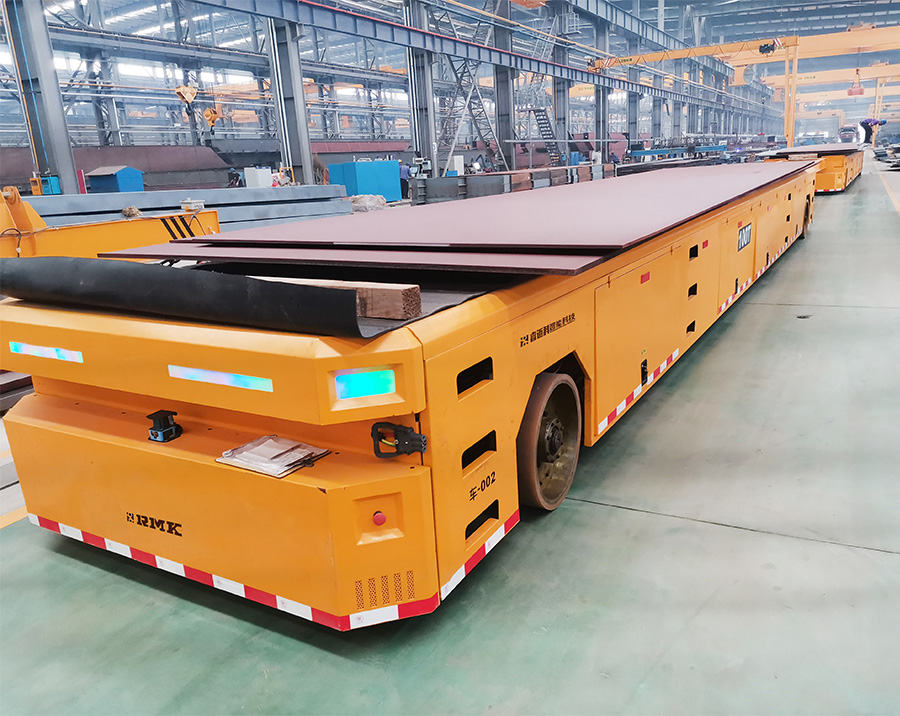

Analyze the Working Environment
Ground Conditions: For flat ground, choose standard wheel systems; for uneven or sloped ground, opt for anti-slip wheels or Rail-type models.
Temperature/Humidity: In high-temperature or humid environments, choose models with corrosion resistance and good heat dissipation.
Explosion-Proof Requirements: In flammable or explosive environments, select explosion-proof transfer carts.
Choose the Operation Method
Manual/Remote Control/Automation: Select the control method based on operational convenience and efficiency requirements. For example, long-distance transportation is recommended to use remote control or automated models.
Safety Requirements
Protective Devices: Such as limit switches, emergency brakes, and anti-collision devices.
Compliance: Ensure the model complies with national or industry safety standards (e.g., CE certification).
Efficiency and Maintenance Needs
Operating Speed: Choose an appropriate speed based on production cycles.
Maintenance Convenience: Opt for modular designs and models with easily replaceable wear parts.
Endurance: For long-distance transportation, consider battery capacity or charging methods.
Select the trolley Type
Standard Electric Industrial Transfer Cart: Suitable for general scenarios, with lower costs.
AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle): Suitable for flexible production lines, requiring navigation systems.
RGV (Rail Guided Vehicle): Suitable for fixed-path, high-precision scenarios.
Rail transfer trolley: Suitable for heavy cargo and long-term fixed routes.
Budget Considerations
All such industrial transfer carts are custom-built to the above-mentioned operational requirements, resulting in significant price variations.Budgets should be formulated based on operational requirements and pricing, or alternatively, suitable models can be selected in accordance with the company’s budget.
Core transfer cart Comparison and Selection Guide
Trolley Type | Core Characteristics | Best Application Scenarios | Key Selection Tips |
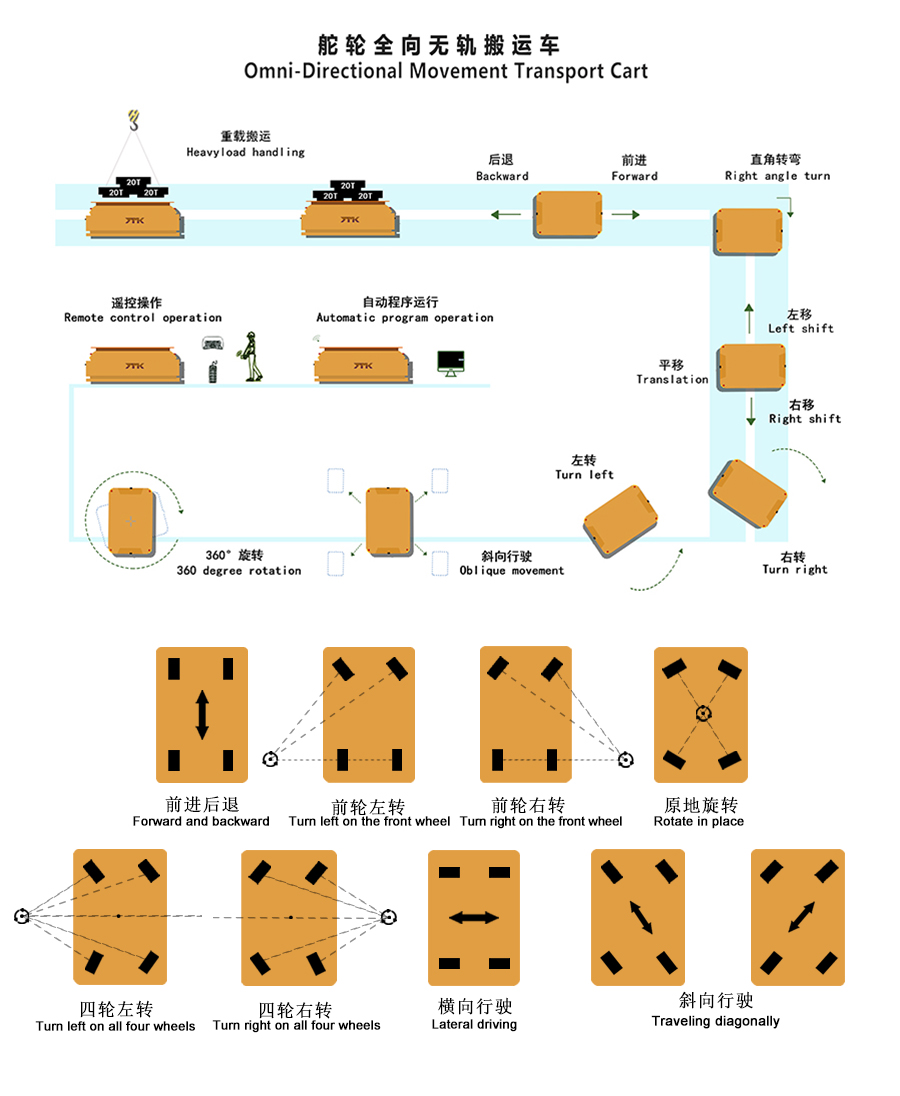
Trackless Electric transfer cart | Flexible and free, powered by batteries or long cables. | Cross-zone, multi-destination material transfer within workshops; scenarios with non-fixed paths. | Focus on turning radius, battery endurance, and ground adaptability. |
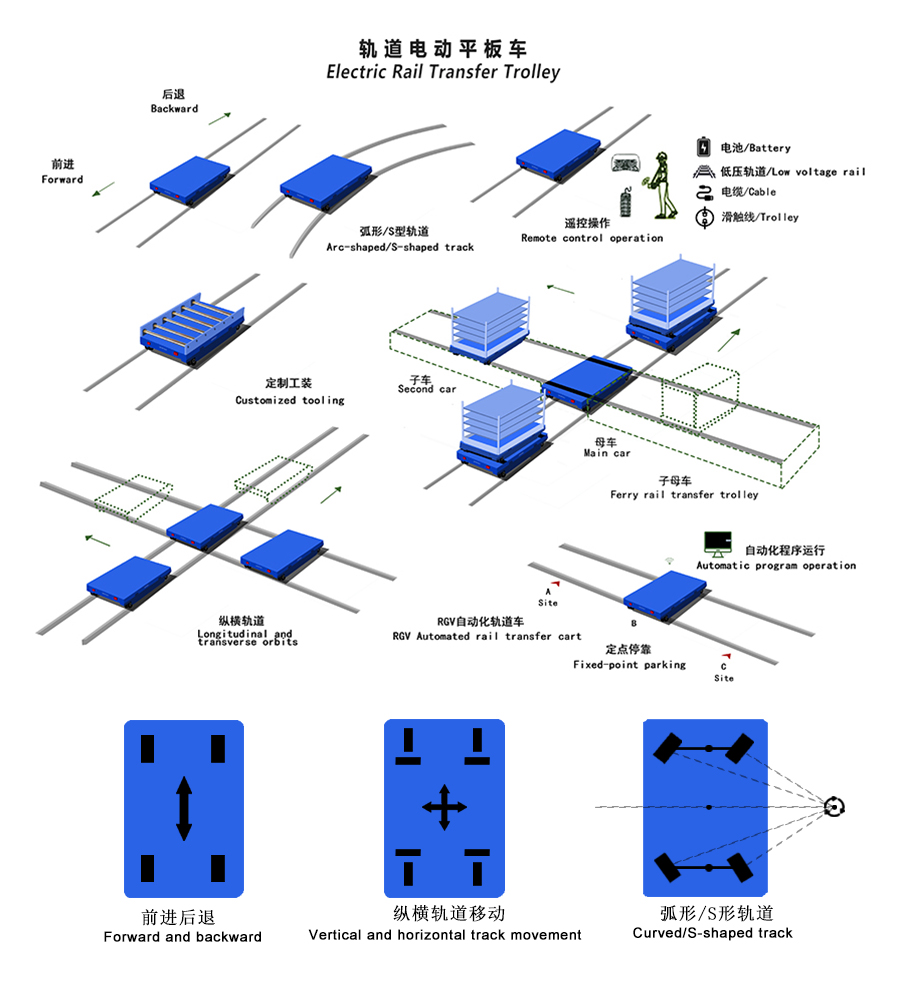
Rail Electric transfer trolley | Precise and reliable, operates on preset tracks, with high load capacity. | Heavy, regular material transport between fixed points (e.g., across workshops or assembly lines). | The choice of power supply method (cable/track/sliding line) is critical. Preferred for heavy-duty transport. |
RGV Rail Guided RGV Shuttle trolley | High-speed and efficient, track-based, can precisely interface with production lines, automated control. | High-tempo assembly lines, automated storage and retrieval systems, frequent delivery to fixed workstations. | Focus on system integration capabilities (communication with PLC, WMS), positioning accuracy, and speed. |
AGV Automated Guided Vehicle | Intelligent and flexible, no physical tracks required, paths are programmable and adjustable. | Smart factories, flexible production lines, human-machine collaborative environments, dynamic scheduling needs. | Navigationmethod(laser/naturalcontour/magnetictape)determinesflexibilityandimplementationcosts.ROIrequiresdetailedevaluation. |
shanghaiShenzhen Mandarin Oriental Hotel
 Humanistic Customized
Humanistic Customized




